Markdown
Markdown is a lightweight markup language for adding formatting elements to plain text. IntelliJ IDEA recognizes Markdown files, provides a dedicated editor with highlighting, completion, and formatting, and shows the rendered HTML in a live preview pane. Support is based on the CommonMark specification .
Enable the Markdown plugin
This functionality relies on the Markdown plugin, which is bundled and enabled in IntelliJ IDEA by default. If the relevant features aren't available, make sure that you didn't disable the plugin.
-
Press Control+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and then select .
-
Open the Installed tab, find the Markdown plugin, and select the checkbox next to the plugin name.
Create a new Markdown file
By default, IntelliJ IDEA recognizes any file with the .md or .markdown extension as a Markdown file.
-
Right-click a directory in the Project tool window Alt+1 and select .
Alternatively, you can select the necessary directory, press Alt+Insert , and then select File .
-
Enter a name for your file with a recognized extension, for example: readme.md .
The Markdown editor provides several basic formatting actions in the floating toolbar that appears when you select a text fragment. You can use the preview pane to see the rendered HTML.

There is also completion for links to files in the current project, for example, if you need to reference source code, images, or other Markdown files. For more information, refer to Links .

Code blocks
To insert a fenced code block, use triple backticks
```
before and after the code block. If you specify the language for the code block, by default, the Markdown editor
injects the corresponding language
.
This enables syntax highlighting and other coding assistance features for the specified language: completion , inspections , and intention actions .

Disable coding assistance in code blocks
If your code blocks are not meant to be syntactically correct, you may want to disable code injection and syntax errors in code blocks.
-
Press Control+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and then select .
-
Clear the following options:
-
Inject languages in code fences
-
Show problems in code fences
-
-
Click OK to apply the changes.
Run commands from Markdown files
When you clone a project, there is usually a README.md file with instructions and commands to run the application, configure your environment, and so on. IntelliJ IDEA detects these commands and provides gutter icons for running the commands.
-
Click the corresponding gutter icon or press Control+Shift+F10 while the caret is at the command that you want to run.

You can disable the gutter icons for running commands in Markdown files in IDE settings Control+Alt+S under : clear the Detect commands that can be run right from Markdown files checkbox.
For more information, refer to Markdown language settings .
Diagrams
The Markdown editor can render diagrams defined with Mermaid and PlantUML . This is disabled by default and requires additional steps.

Enable Mermaid diagram support
-
Press Control+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and then select .
-
Find and install the Mermaid plugin.
Enable PlantUML diagram support
-
Press Control+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and then select .
-
Install and enable PlantUML under Markdown Extensions .
-
After IntelliJ IDEA downloads the relevant extension, click OK to apply the changes.
HTML preview
By default, the Markdown editor shows a preview pane for rendered HTML code based on the Markdown file. You can use
or
in the top right corner of the Markdown editor to show only the editor or the preview pane.
Split editor and preview horizontally
By default, the editor and preview are split vertically (side by side), which is convenient for wide monitors. You can also split it horizontally, so that the preview is displayed in the lower part of the editor, which is more convenient for portrait displays.
-
In the top-right corner of the editor, click
to open the Editor Preview pane.
-
Click
again to split the editor and preview horizontally.

To configure the default layout of the preview, you can use the Preview layout list in .
Disable editor and preview scrollbar synchronization
By default, the scrollbars in the editor and in the preview pane are synchronized, meaning that the location in the preview pane corresponds to the location in the source.
-
Press Control+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and then select .
-
Clear Sync scroll in the editor and preview .
-
Click OK to apply the changes.
Custom CSS
IntelliJ IDEA provides default style sheets for rendering HTML in the preview pane. These style sheets were designed to be consistent with the default UI themes . You can configure specific CSS rules to make small presentation changes (for example, change the font size for headings or line spacing in lists) or you can provide an entirely new CSS to better match your expected output (for example, if you want to replicate the GitHub Markdown style ).

Configure CSS for rendering HTML preview
-
Press Control+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and then select .
-
Configure the settings under Custom CSS :
-
Select Load from to specify the location of a custom CSS file.
-
Select CSS rules rules to enter specific CSS rules that you want to override.
-
-
Click OK to apply the changes.
Here is an example of custom CSS rules:
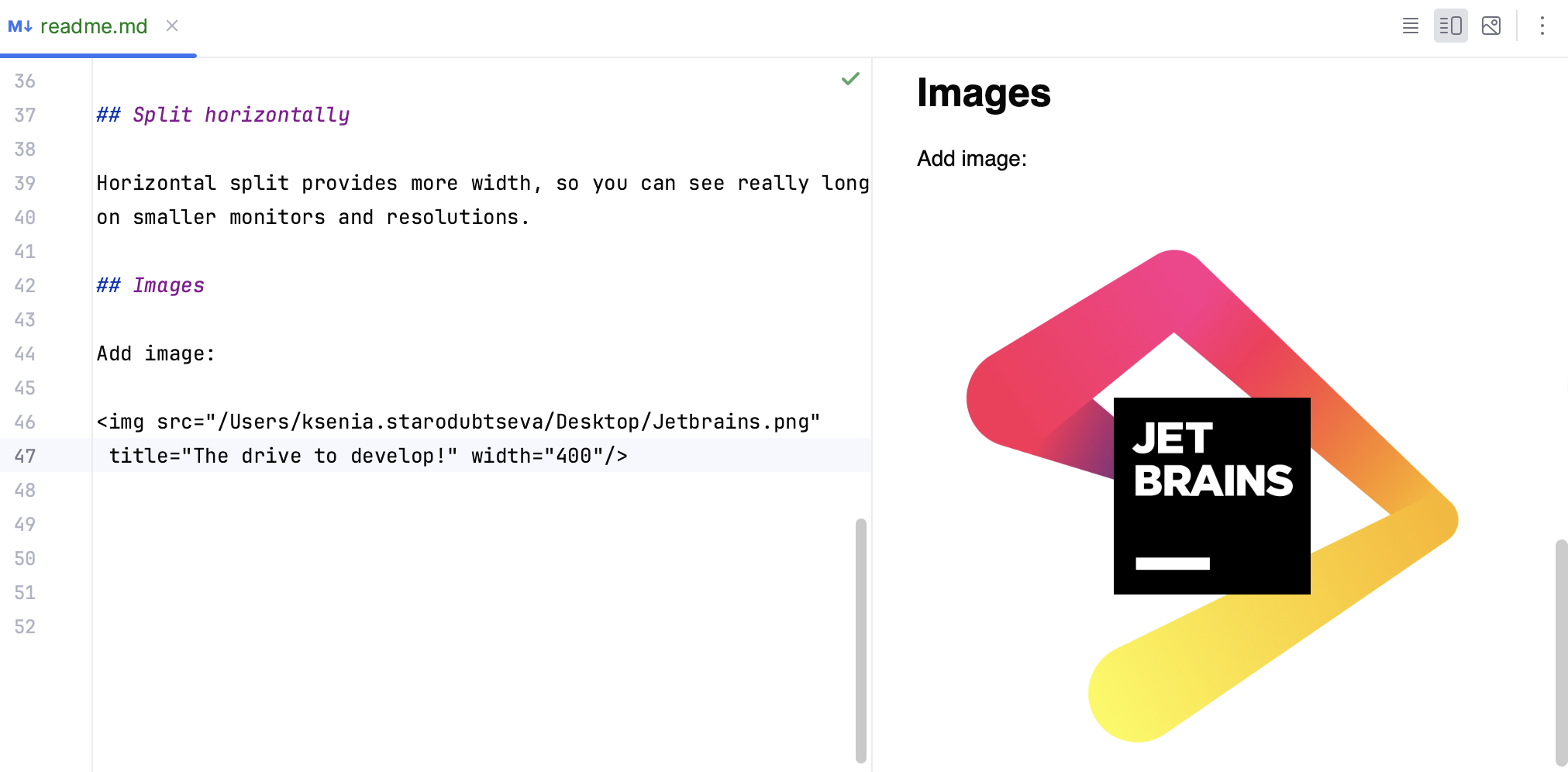
Images
By default, Markdown uses the following syntax for images, which you can enter yourself with completion for paths inside your project:
Insert image
-
Press Command U .
Alternatively, press Alt+Insert to open the Insert… popup, and select Image .
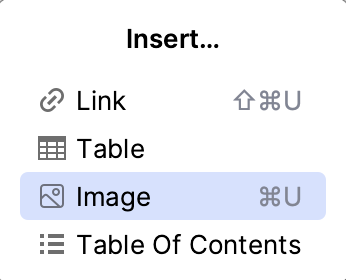
-
Specify the path to the image in the Insert Image dialog.
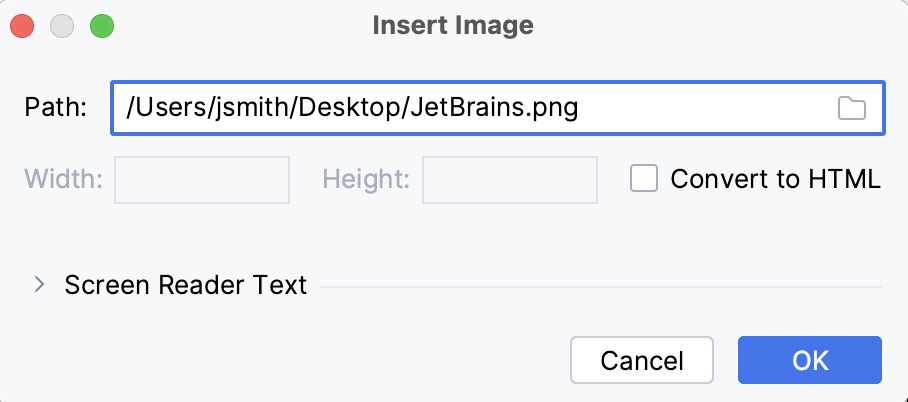
-
Click OK .
To configure the image, click
in the gutter on the line where the image is inserted. For example, you can select
Convert to HTML
in the
Insert Image
dialog to insert the image with raw HTML markup in the Markdown file.
This will produce the following:
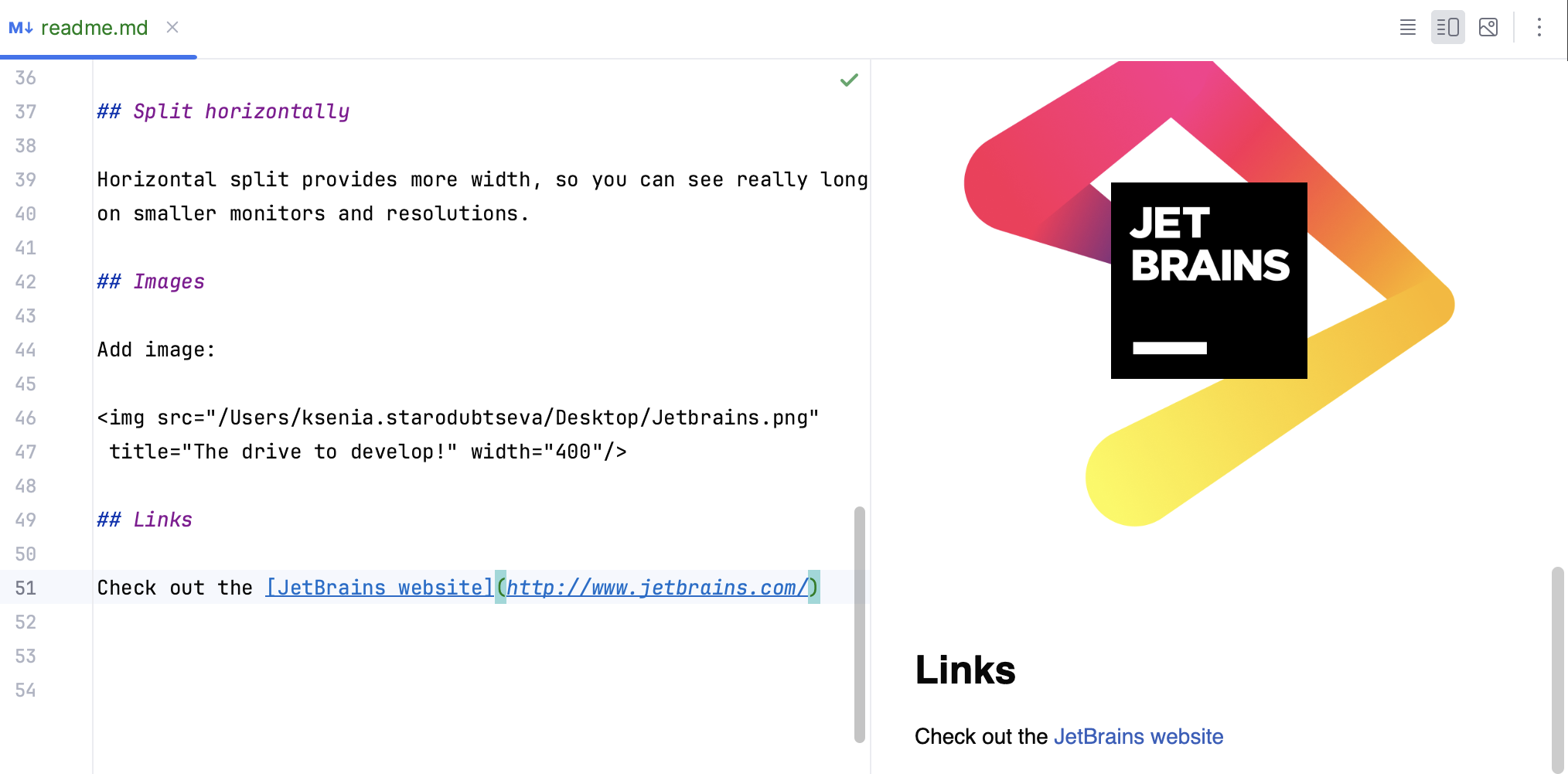
Links
You can define links with the following syntax:
Insert link
-
Press Command Shift U .
Alternatively, press Alt+Insert to open the Insert… popup, and select Link .

If you had some text highlighted, it will be enclosed in
[ ]
as the text of the link. If you had a URL copied to the clipboard, it will be enclosed in
( )
as the link URL.
The optional title appears when you hover over the link.
Link to other files and headers
-
Besides URLs, you can add links to any header in the current file:
# This is a chapter Link to [this chapter](#this-is-a-chapter) -
You can also link to any other file relative to the current file:
# This is a chapter Link to [a chapter in another file](another-file.md#some-chapter)
IntelliJ IDEA provides completion for link labels that are available in the current context: files relative to the current file and valid header labels.
Control+LeftClick on a link label to navigate to the referenced header.
You can invoke Find Usages Alt+F7 on a header or label to see all the links pointing to this label. You can also invoke the Rename refactoring Shift+F6 on a header or label to rename it along with all relevant usages.
Generate table of contents
You can generate a properly indented list of headers available in the current file.
-
Place the caret where you want to add the table of contents for the current file and press Alt+Insert to open the Insert… popup.
-
Select Table of Contents .
If you already have a table of contents in this file, select Update Table of Contents to update it after you add, remove, or rename some headers.
The table of contents is enclosed in
<!-- TOC -->
comment tags.